What is heart failure?
The term “heart failure” can be frightening. It doesn’t mean the heart has “failed” or stopped working. It means the heart doesn’t pump as well as it should.
If you have heart failure, you’ll enjoy better health and quality of life if you take care of yourself and keep yourself in balance. It’s important to learn about heart failure, how to keep in good balance, and when to call the doctor.
Heart failure and aging
Although the risk of heart failure does not change as you get older, you are more likely to have heart failure when you are older.
Symptoms
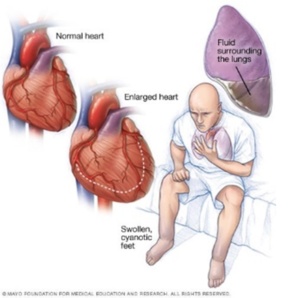
Heart failure can be ongoing (chronic), or it may start suddenly (acute).
Heart failure signs and symptoms may include:
- Shortness of breath with activity or when lying down
- Fatigue and weakness
- Swelling in the legs, ankles and feet
- Rapid or irregular heartbeat
- Reduced ability to exercise
- Persistent cough or wheezing with white or pink blood-tinged mucus
- Swelling of the belly area (abdomen)
- Very rapid weight gain from fluid build-up
- Nausea and lack of appetite
- Difficulty concentrating or decreased alertness
- Chest pain if heart failure is caused by a heart attack
Risk factors
A single risk factor may be enough to cause heart failure, but a combination of factors also increases your risk.
Risk factors for heart failure include:
- Coronary artery disease.Narrowed arteries may limit your heart’s supply of oxygen-rich blood, resulting in weakened heart muscle.
- Heart attack.A heart attack is a form of coronary artery disease that occurs suddenly. Damage to your heart muscle from a heart attack may mean your heart can no longer pump as well as it should.
- Heart valve disease.Having a heart valve that doesn’t work properly raises the risk of heart failure.
- High blood pressure.Your heart works harder than it has to if your blood pressure is high.
- Irregular heartbeats.These abnormal rhythms, especially if they are very frequent and fast, can weaken the heart muscle and cause heart failure.
- Congenital heart disease.Some people who develop heart failure were born with problems that affect the structure or function of their heart.
- Having diabetes increases your risk of high blood pressure and coronary artery disease. Don’t stop taking any medications on your own. Ask your doctor whether you should make changes.
- Alcohol use.Drinking too much alcohol can weaken the heart muscle and lead to heart failure.
- Sleep apnea.The inability to breathe properly while you sleep results in low blood-oxygen levels and an increased risk of irregular heartbeats. Both of these problems can weaken the heart.
- Smoking or using tobacco.If you smoke, quit. Using tobacco increases your risk of heart disease and heart failure.
- People who have obesity have a higher risk of developing heart failure.
- Certain viral infections can cause damage to the heart muscle.
Complications
Complications of heart failure depend on the severity of heart disease, your overall health and other factors such as your age. Possible complications can include:
- Kidney damage or failure.Heart failure can reduce the blood flow to your kidneys, which can eventually cause kidney failure if left untreated. Kidney damage from heart failure can require dialysis for treatment.
- Heart valve problems.The valves of the heart, which keep blood flowing in the right direction, may not work properly if your heart is enlarged or if the pressure in your heart is very high due to heart failure.
- Heart rhythm problems.Heart rhythm problems may lead to or increase your risk of heart failure.
- Liver damage.Heart failure can cause fluid build-up that puts too much pressure on the liver. This fluid backup can lead to scarring, which makes it more difficult for your liver to work properly.
Prevention
The key to preventing heart failure is to reduce your risk factors. You can control or eliminate many of the risk factors for heart disease by making healthy lifestyle changes and by taking the medications prescribed by your doctor.
Lifestyle changes you can make to help prevent heart failure include:
- Not smoking
- Controlling certain conditions, such as high blood pressure and diabetes
- Staying physically active
- Eating healthy food along with cut down salt intake
- Maintaining a healthy weight
- Reducing and managing stress
Disclaimer: The information in no way constitutes, or should be interpreted as medical advice. Nor is the above article an endorsement of any research findings and source publications.